Medications for Kidney Stone Prevention
In some patients, the addition of a daily medicine may be recommended by their provider to decrease the risk of future stones. In clinical trials, these medications have been shown to significantly reduce or prevent the number of stones events a patient may experience.
While many patients are reluctant to take medications and prefer to focus on dietary modification, medications can be a good option, especially in individuals who frequently develop new stones.

Common Preventative Medications
Potassium citrate and sodium bicarbonate
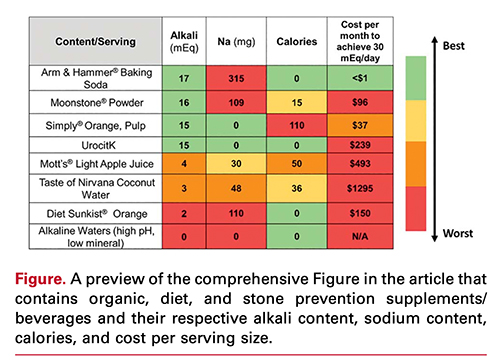
These are the most common agents used to increase urine pH. Many drinks and supplements listed below may achieve the same goal, but note, some drinks listed as alkaline actually do not provide a citrate load or raise urine pH
How does it work: Alkali has two beneficial effects in stone formers. It increases urinary citrate, which acts a direct inhibitor of stone formation of calcium oxalate stones. It also increases urine pH, making urine more alkaline which helps to dissolve uric acid.
How well does it work: In four randomized studies with a total of 227 patients on citrate medications or placebo, treatment reduced the recurrence of stones from 65% to 46.5% after at least one year of treatment. In two randomized studies with a total of 104 patients who were treated with citrate medication after stone surgery, the recurrence rate of stones was 72.5% in those on placebo and 34% in those on medication. (Mattle and Hess, Urol Res, 2005)
Side effects: The primary side effects of kcitrate is gastric irritation, less so with the tablet which contains potassium citrate in a wax matrix. If you are just starting potassium citrate, one should make sure to get labs to check their blood level of potassium
How does it work: Thiazides including hydrochlorothiazide, chlorthalidone, and indapamide, stimulate calcium reabsoprtion in the kidney, reducing the concentration of calcium in the urine.
How well does it work: Several studies have shown that Thiazides can effectively reduce stone growth, reduce stone events, lower urinary calcium and improve bone density. Thiazides will work best on a low salt diet.
Side effects: Thiazide treatment can cause a decrease in blood potassium levels and can also can reduce citrate levels in the urine. Therefore, potassium citrate is sometimes given with thiazides to correct both the low potassium and citrate that can occur with its use. Fatigue and dizziness and other side effects have also been reported by patients on thiazide treatment.
Useful for: Elevated urine uric acid (hyperuricosuria), uric acid stones, and mixed uric acid and calcium stones.
How does it work: Allopurinol interferes with the conversion of xanthine (a purine) to uric acid with a resulting decrease in uric acid levels in urine. It is more commonly used in patients with gout. Purines are found at high concentrations in meats, seafood, and beer. Uric acid in urine can directly form uric acid stones or can act as an promoter of calcium oxalate stones. Most providers treat uric acid stones with Kcitrate, or an alternative alkali source first. If someones blood level of uric acid is elevated or their urinary uric acid is very elevated providers can use Allopurinol to prevent uric acid stones.
How well does it work: In a randomized study of 60 patients with high urinary uric acid and a history of calcium stones, 31% of those on treatment developed new stones over three years compared to 58% of those on placebo. Those on treatment also had a longer time before re-developing a stone (Ettinger et al, NEJM, 1986).
Side effects: Allopurinol can cause GI upset, diarrhea, and drowsiness in addition to other potential side effects.
Research Articles
Stay Involved
Nearly 10% of the United States population has suffered from stones. You can help connect with our community and support our mission to accelerate kidney stone research.
Complete the form to learn more about KSC and its initiatives.
By submitting this form, you consent to receive educational emails, research updates, and event invitations from Kidney Stone Collaborative. We will never sell or share your information with third parties. You may unsubscribe at any time.
Information provided is for educational purposes only and is not a substitute for medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personal medical concerns.